The complete PDF of the HSE Plus two Focus Area syllabus. The syllabus is the detailed study material for the courses offered under Higher Secondary subject and the plus two focus areas as well. The examination conducted by the Kerala State Higher Secondary Education Board (Kerala Syllabus) is in these subjects in which students have to study a lot thoroughly and intensely, and the knowledge thus gained has to be passed on to one's parents and teachers. This syllabus has been designed considering it all. As per this syllabus, there is a need for a lot of study and practice.
Plus Two Focus Area Syllabus(toc)
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two ( Science ) Focus Area
The Kerala High School Board and SCERT have selected certain areas to focus on preparing students for the Plus Two exam. As the schools do not operate in the current academic year and the classes are conducted entirely on the online platform, the students are struggling to cope with the entire elements assigned for the upcoming examination on the High Board. So to make things easy the government chose some areas as centralized areas and for the next study, 90% of questions are expected to come from the selected topics in each chapter.
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two Focus Area - English
| Lesson | Focus Area |
| 1 | The 3Ls of Empowerment (Speech) |
| 2 | Any Woman (Poem) |
| 3 | Matchbox (Story) |
| 4 | Horegallu (Anecdote) |
| 5 | Mending Wall [Poem] |
| 6 | The Hour of Truth [One Act Play] |
| 7 | A Three-Wheeled Revolution [ Interview ] |
| 8 | Rice (Poem) |
| 9 | Dangers of Drug Abuse [ Essay] |
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two Focus Area - Hindi
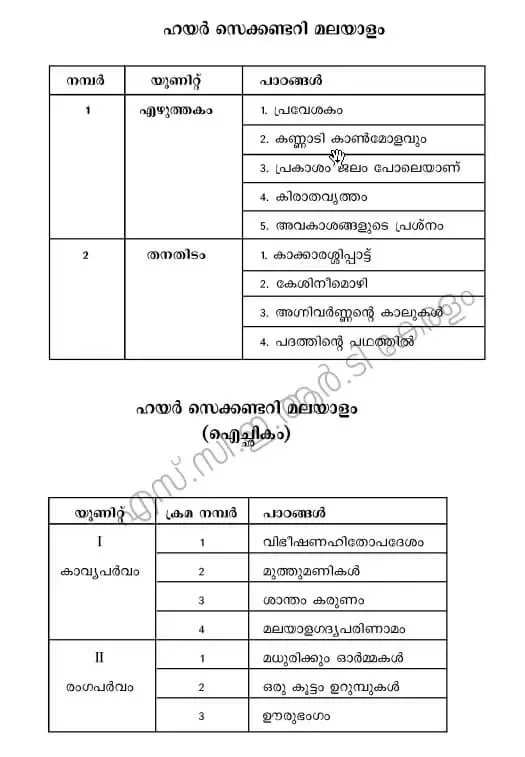
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two Focus Area - Malayalam
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two Focus Area - Physics
| Electric Charges and Fields |
1.2 Electric Charge 1.5 Basic Properties of Charge 1.6 Coulomb’s Law 1.8 Electric Field 1.9 Electric Field Lines 1.10 Electric Flux 1.11 Electric Dipole 1.14 Gauss’s Law 1.15 Applications of Gauss’s Law |
| Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance | 2.2 Electrostatic Potential 2.3 Potential Due to a Point Charge 2.6 Equipotential Surfaces 2.11 Capacitors and Capacitance 2.12 The Parallel Plate Capacitor 2.14 Combination of Capacitors 2.15 Energy Stored in a Capacitor |
| CURRENT ELECTRICITY |
3.4 OHM ‘S LAW 3.9 ELECTRICAL ENERGY, POWER 3.10 COMBINATION OF RESISTORS-SERIES AND PARALLEL 3.11 CELLS, EMF, INTERNAL RESISTANCE 3.13 KIRCHHOFF’S RULES 3.14 WHEATSTONE BRIDGE 3.15 METER BRIDGE 3.16 POTENTIOMETER |
| MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM |
4.2 MAGNETIC FORCE 4.5 MAGNETIC FIELD DUE TO A CURRENT ELEMENT, BIOT -SAVART LAW 4.6 MAGNETIC FIELD ON THE AXIS OF A CIRCULAR CURRENT LOOP 4.7 AMPERE’S CIRCUITAL LAW 4.8 THE SOLENOID AND THE TOROID |
| MAGNETISM AND MATTER |
5.3 MAGNETISM AND GAUSS’S LAW 5.4 THE EARTH’S MAGNETISM 5.5 MAGNETISATION AND MAGNETIC INTENSITY |
| ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION |
6.4 FARADAY’S LAW OF INDUCTION 6.6 MOTIONAL ELECTROMOTIVE FORCE 6.8 EDDY CURRENTS 6.10 AC GENERATOR |
| ALTERNATING CURRENT |
7.2 AC VOLTAGE APPLIED TO A RESISTOR 7.3 REPRESENTATION OF AC CURRENT AND VOLTAGE BY ROTATING VECTORS-PHASORS 7.4 AC VOLTAGE APPLIED TO AN INDUCTOR 7.5 AC VOLTAGE APPLIED TO A CAPACITOR 7.9 TRANSFORMERS |
| ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES | 8.2 DISPLACEMENT CURRENT 8.3 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE |
| RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS |
9.2 REFLECTION OF LIGHT BY SPHERICAL MIRRORS 9.3 REFRACTION 9.5 REFRACTION AT SPHERICAL SURFACES AND BY LENSES 9.6 REFRACTION THROUGH A PRISM |
| WAVE OPTICS |
10.2 HUYGENS PRINCIPLE 10.3 REFRACTION AND REFLECTION OF PLANE WAVES USING HUYGENS PRINCIPLE 10.7 POLARISATION |
| DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER |
11.3 PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT 11.6 EINSTEIN’ S PHOTOELECTRIC EQUATION: ENERGY QUANTUM OF RADIATION 11.7 PARTICLE NATURE OF LIGHT: THE PHOTON |
| ATOMS |
12.4 BOHR MODEL OF THE HYDROGEN ATOM 12.6 DE BROGLIE’S EXPLANATION OF BOHR’S SECOND POSTULATE OF QUANTISATION |
| NUCLEI | 13.6 RADIOACTIVITY 13.7 NUCLEAR ENERGY |
| SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS |
14.7 APPLICATION OF JUNCTION DIODE AS A RECTIFIER 14.9 DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND LOGIC GATES |
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two Focus Area - Chemistry
| Name of Chapter | Focus Area |
| The solid-state |
1.2 Amorphous and crystalline solids 1.4 Crystal lattices and unit cells 1.5 Number of atoms in a unit cell 1. 6 Close packed structures 1.9 Imperfections in solids 1.10 Electrical properties 1.11 Magnetic properties |
| Solutions |
2. 3. 2 Solubility of gas in liquids 4 Vapour pressure of liquid solutions 2.5 Ideal and non-ideal solutions 2.6 Colligative properties and determination of molar mass |
| Electrochemistry |
3.3 Nernst equation 3. 4. 2. Variation of conductivity and molar conductivity with concentration 3.6 Batteries 3.7 Fuel cells 3.8 Corrosion |
| Chemical kinetics |
4. 2 Factors influencing the rate of a reaction 4.3.2 First order reactions and their half-life period 4.4 Pseudo first-order reaction 4.5 Temperature dependence of the rate of reaction- Arrhenius equation |
| Surface chemistry |
5.1 Adsorption 5.2 Catalysis 5.4 Classification of colloids 5.5 Emulsions |
| General principles and Process of Isolation of elements – |
6.2 Concentration of ores 6.3 Extraction of crude metal from concentrated ore elements 6.4. 1 Ellingham diagram – extraction of Iron 6.5 Hall Heroult process (extraction of Al) 6. 7 Refining
|
| The P-block elements |
7.3 Ammonia 7.5 Nitric acid 7.8 Phosphorus halides 7.17 Sulfuric acid 7. 22 Inter halogen compounds 7.23 Group 18 elements- Xenon halides |
| The d-and f-block elements |
8.3 Magnetic properties, formation coloured ions, formation complexes,
catalytic property 8.4 Potassium permanganate and potassium dichromate 8.5.2 Atomic and ionic sizes 8.7 Some applications of d- and f-block elements |
| Coordination compounds |
9.3 Nomenclature of coordination compounds 9.4 Isomerism in coordination compounds 9.5.2 Magnetic properties of coordination compounds 9.8 Importance and applications of coordination compounds |
| Haloalkanes and haloarenes |
10.4.1 Preparation from alcohols 10.4.2 Preparation from hydrocarbons 10.6.1 Reactions of haloalkanes (Nucleophilic substitution) 10.6.2 Reactions of haloarenes (Electrophilic substitution) 10.7.2 Trichloro methane |
| Alcohols, phenols and ethers |
11.4.1 Preparation of alcohols( from alkenes, carbonyl compounds and
Grignard reagent 11.4.2 Preparation of phenol (from haloarenes and diazonium salts) 11.4.4 Chemical reactions (Lucas test, dehydration, nitration of phenol. Reimer Tiemann reaction) 11.5 Commercially important alcohols- ethanol 11.6.1 Preparation of ethers-Williamson synthesis 11.6.3 Chemical reactions (Friedel Crafts reaction) |
| Aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids |
12.2 Preparation of aldehydes and ketones ( By oxidation of alcohols, by
deHydrogenation of alcohols, Rosenmund reduction, Etard reaction,
Gatterman-Koch reaction, Friedel Craft’s reaction) 12.4 Chemical reactions (Reduction, Oxidation, Aldol reaction, Cannizzaro reaction) 12.7 Preparation of Carboxylic acid (from aldehydes and ketones, from alkyl benzene) 12.9 Chemical reactions (acidity, reaction with ammonia, Kolbe electrolysis, Hell-Volhard Zelinsky reaction. Ring substitution) |
| Amines |
13.4 Preparation of amines (Reduction of nitriles, amides, Hoffmann
Bromamide reaction) 13.6 Chemical reactions ( carbylamine reaction, Ilinsbergtest. Electrophilic substitution) 13.9 Chemical reactions of diazonium salts- sandmaeyer reaction, the coupling reaction |
| Biomolecules |
14.1.1 Classification of carbohydrates 14.1.2 Monosaccharides (Preparation of glucose from sucrose) 14.1.3 Disaccharides (glycosidic linkage, invert sugar) 14.1.4 Starch, glycogen 14.2.4 Denaturation of protein 14.5.1 Chemical composition of nucleic acids |
| Polymers |
15.1 Classification of polymers Addition and condensation polymers ( Teflon, Nylon6,6, Nylon 6, PVC, polystyrene, Polyethene) 15.2.4 Rubber ( Natural rubber, vulcanisation) 15.4 Biodegradable polymers |
| Chemistry in Everyday life |
16.3.1 Antacid 16.3.3 Neurologically active drugs 16.3.4 Antimicrobials( antiseptics, disinfectants) |
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two Focus Area - Maths
| Chapter | Focus area |
| RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS |
1.3 Types of Functions 1.4 Composition of Functions and Invertible Function |
| INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS | 2.3 Properties of Inverse Trigonometric Functions |
| MATRICES |
3.2 Matrix 3.3 Types of Matrices 3.4 Operations on Matrices 3.5 Transpose of a Matrix 3.6 Symmetric and Skew Symmetric Matrices |
| DETERMINANTS |
4.2 Determinant 4.5 Minors and Cofactors 4.6 Adjoint and Inverse of a Matrix 4.7 Applications of Determinants and Matrices |
| CONTINUITY AND DIFFERENTIABILITY |
5.2 Continuity 5.3 Differentiability 5.8 Mean Value Theorem |
| APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES |
6.2 Rate of Change of Quantities 6.3 Increasing and Decreasing Functions 6.4 Tangents and Normals |
| INTEGRALS |
7.3.1 integration by substitution 7.4 Integrals of Some Particular Functions 7.9 Evaluation of Definite Integrals by Substitution |
| APPLICATION OF INTEGRALS |
8.2 Area under Simple Curves |
| DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS |
9.2 Basic Concepts 9.5.1 Differential equations with variables separable |
| VECTOR ALGEBRA |
10.4 Addition of Vectors 10.5 Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar 10.6 Product of Two Vectors |
| THREE DIMENSIONAL GEOMETRY |
11.3 Equation of a Line in Space 11.5.1 Distance between skew lines 11.6.2 Equation of a plane perpendicular to a given vector and passing through a given point 11.6.3 Equation of a plane passing through three non-collinear points |
| LINEAR PROGRAMMING |
12.2.2 Graphical method of solving linear programming problems |
| PROBABILITY | 13.2 Conditional Probability 13.4 independent Events |
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two Focus Area - Botany
| Name of Chapter | Focus Area |
| Reproduction in organisms |
1.1. Asexual reproduction 1.2.1. Gametogenesis 1.2.2. Fertilisation. |
| Sexual reproduction in flowering plants |
2.2.1 . Structure of microsporangium. Structure of pollen grain 2.2.2. Megasporangium-structure, megasporogenesis, Female gametophyte 2.2.3. Pollination-Classification based on the source of pollen (Autogamy, geitonogamy and xenogamy) and agents of pollination (wind, water and insects -peculiarities with examples) and artificial hybridisation 2.3. Double fertilisation 2.4.2. Embryo- structure 2.4.3. False fruit, True fruit and Parthenocarpic fruit |
| Strategies for enhancement in food production |
9.1.1. Dairy farm management 9.1.3. Beekeeping 9.2. Plant breeding- main steps 9.2.4. Plant breeding for improved food quality 9.3 S.C.P 9.4.Tissue culture |
| Biotechnology- Principles and processes |
11.2. Tools of recombinant DNA technology 11.2.1.Restriction enzymes,
Gel electrophoresis. 11.3 . Processes of rDNA technology 11.3.3. Amplification of gene of interest using PCR, 11.3.5.Obtaining the foreign gene product |
| Biotechnology and its applications |
12.1. Biotechnological applications in agriculture-Uses of GMOs and Bt
cotton 12.2.1. Genetically engineered insulin. 12.2.2. Gene therapy |
| Organisms and Populations |
13 1.3. Adaptations -In organisms of deserts, polar regions and high
altitudes 13.2.1 Population attributes- Age pyramids and population density 13.2.2. Population growth (Up to population growth equation) 13.2.4. Population interactions – Parasitism, Commensalism and Mutualism |
| Ecosystem |
14.2. Productivity 14.3. Decomposition 14.4. Energy flow -Food chain, Food web and Trophic levels 14.5. Ecological pyramids. 14.7. Nutrient cycling -Phosphorus cycle |
| Environmental issues |
16.2. Water pollution and its control, BOD, Algal bloom and
Eutrophication 16.6. Greenhouse effect and global warming 16.7. Ozone depletion in the stratosphere 16.9. Deforestation |
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two Focus Area - Zoology
| Name of the Chapter | Focus Area |
| Human reproduction |
3.1 Male reproductive system (Location of testes & its significance;
Cells lining Seminiferous tubules & their function; Duct System)
3.2 The female reproductive system (Oviduct, Uterus, Significance of Hymen) 3.3 Gainetogenesis (Spermatogenesis, Oogenesis, Role of Hormones -FSH & LH in Spermatogenesis; Structure of Sperm ) 3.4 Menstrual cycle (Hormones involved) 3.5 Fertilization and implantation (Site of fertilization; Morula; Structure of Blastocyst) 3.6 Pregnancy and embryonic development (Placenta, hCG, hPL, Relaxin ) 3.7 Parturition & Lactation (Colostrum) |
| Reproductive health |
4.1 Reproductive health problems and strategies (Amniocentesis) 4.2 Population explosion and birth control (IMR, MMR; Birth Control Measures – Natural, Barrier, IUD’s, Oral Contraceptives, Surgical methods.) 4.3 Medical Termination of Pregnancy (What is MTPjWhy MTP) 4.4 Sexually transmitted diseases (Examples of STD; Measures to avoid STD’s) 4.5 Infertility(Assisted Reproductive Technologies in detail) |
| Principles of inheritance and variation |
5.1 Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance(TabIe 5.1 Contrasting Traits studied by
Mendel in Pea 5.2 Inheritance of one gene (Allele, Genotype, Phenotype) 5.2.2.1 Incomplete dominance (Definition, Ratio & Cross only) 5.2.2.2 Co-dominance (Blood Grouping in Fable 5.3) 5.3.2 Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance (Reasons for selecting Drosophila as the experimental material by Morgan) 5.4.1 Sex determination in Humans 5.6.1 Pedigree analysis 5.6.2 Mendelian disorders (Sickle Cell Anaemia, Haemophilia) 5.6.3 Chromosomal disorders (Down’s Syndrome, Klinefelter’s Syndrome, Turner’s Syndrome) |
| Molecular basis of inheritance |
6.1.1 Structure of polynucleotide chain (Salient Features of Double
Helix structure of DNA; Central Dogma) 6.1.2 Packaging of DNA helix – (Structure of Nucleosome – Diagram & Explanation alone; Euchromatin; Heterochroniaiiu) 6.2 The Search For Genetic Material (Transforming Principle) 6.2.1 The Genetic Material is DNA (Hershev-Chase Experiment) 6.4.2 The Machinery and the Enzymes (DNA dependent DNA polymerase; Replication fork; DNA Ligase) 6.5.1 Transcription unit( Promoter, Terminator, Structural Gene) 6.5.2 Transcription unit & the Gene (Introns. Exons) 6.6 Genetic code – Salient Features 6.8.1 The Lac Operon 6.9 Human Genome Project(Expansion of HGP, BAC & YAC) 6.10 DNA fingerprinting (Steps; Application) |
| Evolution |
7.1 Origin of life (Urey-Miller experiment) 7.3 What is the evidence of evolution? (Homologous organs & Analogue organs with eggs; Observation supporting natural selection – Moths in the unpolluted area and polluted areas in England) 7.7 Hardy Weinberg principle (Equation; 5 factors affecting Hardy Weinberg equilibrium) 7.9 Origin and Evolution of man (Names alone in sequential order up to Homo sapiens) |
| Human health and disease |
8.1 Common diseases in humans (Typhoid, Malaria) 8.2.1 Innate Immunity ( Four types of Barriers) 8.2.2 Acquired Immunity (Structure of an Antibody molecule Diagram) 8.3 AIDS (Transmission; Test for AIDS; Prevention) 8.4 Cancer(Benign tumour, Malignant Tumor, Treatment of cancer) 8.5.3 Effects of drug/alcohol abuse |
| Microbes in human welfare |
10.1 Microbes in Household Products (LAB) 10.2.3 Chemicals enzymes and other bioactive molecules 10.5 Microbes as biocontrol agents – Bacillus thuringiensis, Trichoderma |
| Biodiversity and Conservation |
15.1.2 (ii) Species- area relationship (graph and equation) 15.1.3 the importance of species diversity to the ecosystem (Rivet Popper Hypothesis) 15.1.4 Loss of biodiversity- (Causes of biodiversity losses/Evil Quartet) 15.2.2 How do we conserve biodiversity (In situ conservation, Ex-situ conservation) |
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two Focus Area - Computer Science
| Chapter | Focus Area |
| 1. Structures and Pointers | Concept of structure and example, Defn of Pointer, Use of & and * operators, Static V/s dynamic memory allocation, new and delete operators |
| 2. Concept of Object-Oriented Programming | POP V/s OOP, five concepts of OOP |
| 3. Data Structures and Operations | Classification of data structures. Operations on data structures, Concept of the stack, queue (linear only) and linked list. Push and Pop operations with algorithms. |
| 4. Web Technology | Static and Dynamic web pages, Comparison of Client-side and Server-side scripts, Structure of HTML code, Container tags and empty tags, Common attributes of <BODY> tag, Use of important tags(Headings, <BR>, <P>, <HR>, text formatting tags, <MARQUEE>, <FONT>,<IMG>), Only the essential attributes need to be considered. |
| 5. Web Designing using HTML | List (Ordered, Unordered, Definition), <A> tag Ir4d HREF attribute. Definition of internal and external linking, Table tags, Listing and use of Input controls in Form, Coding questions may focus only on simple lists and simple tables. |
| 6. Client-side Scripting using JavaScript | <SCRIPT> tag, Data types, var keyword, Operators, Control structures and Built-in functions |
| 7. Web Hosting | Types of web hosting, FTP client software, Free hosting |
| 8. Database Management System | Advantages of the database, Components of DBMS, Types of users, RDBMS terminologies, Relational operations (Select, Project, Union, Intersection) |
| 9. Structured Query Language | SQL components, SQL data types, Constraints, Use of commands (DDL-CREATE TABLE, DROP TABLE; DML – SELECT, DELETE, UPDATE with essential clauses only). SQL queries are to be avoided. |
| 10. Server-side Scripting using PHP | echo() V/s print, PHP data types, Operators and Control structures |
| 11. Advances in Computing | Serial V/s Parallel computing, Cloud computing and three services, Applications of computational intelligence – listing only |
| 12. ICT and Society | Applications of ICT – Education, Business, Governance. Cybercrimes against individuals. |
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two ( Commerce ) Focus Area
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two Focus Area - Accountancy
Part 1- Accounting
-
Accounting for Not-for-Profit Organisation
Meaning and Characteristics of Not-for-Profit Organisation
Accounting Records of Not-for-Profit Organisations
Receipt and Payment Account
Income and Expenditure Account
The distinction between Income and Expenditure A/c and Receipt and Payment A/c
Treatment of Subscription in the financial statements of Not for profit organisation -
Accounting for Partnership – Basic Concepts
Nature of partnership
Partnership deed
Provisions of Partnership Act Relevant for Accounting
Maintenance of Capital Accounts of Partners
The distinction between Fixed and Fluctuating Capital Accounts
Profit & Loss Appropriation Account -
Reconstitution of Partnership – Admission of a Partner
Modes of Reconstitution of a Partnership Firm
Admission of a New Partner
New profit sharing ratio & Sacrificing ratio
Goodwill – Factors Affecting the Value of Goodwill
Methods of valuation of goodwill (Average Profit)
Treatment of goodwill (When the new Partner brings goodwill in cash.)
Adjustment for Accumulated Profits and Losses
Revaluation of Assets and Reassessment of Liabilities
Preparation of Revaluation account. Partners Capital Account & Balance sheet -
Reconstitution of Partnership -Retirement & Death of a partner
New profit sharing ratio & Gaining ratio
Adjustment for Revaluation of Assets and Liabilities
Adjustment of Accumulated Profits and Losses
Disposal of Amount Due to Retiring Partner
Preparation Partner’s Loan Account
Death of a partner – Calculation of amount due to the deceased partner -
Dissolution of Partnership Firm
Dissolution of Partnership
Dissolution of a Firm
The distinction between Dissolution of partnership and dissolution of firm
Preparation of Realisation A/c
Part II Company Accounts and Analysis of Financial Statements
-
Accounting for share capital
Features and types of companies
Share capital and its categories
Issue of shares – basic journal entries
Calls in arrears and calls in advance
Issue of shares at par and at a premium
Oversubscription of shares (Excluding pro-rata)
Forfeiture and Re-issue of shares -
Issue and redemption of debentures
Meaning and types of debentures
Difference between shares and debentures
Issue of debentures for cash -
Financial statements of a company
Types of financial statements
Balance sheet and P&L account
Limitation of financial statements -
Analysis of Financial statements
Objectives of Analysis of Financial Statements
Tools of Analysis of Financial Statements
Comparative statements
Common size statements
Limitation of AFS -
Accounting Ratios
Meaning, advantages and limitations of ratio analysis
Liquidity ratio (Current ratio Liquid ratio)
Solvency ratio (Debt equity ratio and Proprietary ratio)
Activity ratio (Inventory turn over and Working capital turn over ratio)
Profitability ratio (Gross profit Ratio, Net Profit Ratio) -
Cash flow statements
Meaning, objectives and benefits of Cash flow statements
Classification of activities for Cash flow statements
Limitation of Cash flow statements
Part III Computerized Accounting
-
Overview of Computerised accounting system
Features of CAS
Components of CAS
Grouping of Accounts
Codification of Accounts
Merits and Demerits of CAS. -
Spread Sheet
Features of LibreOffice Calc
Components of LibreOffice Calc
Spread Sheet Operations
Cell references
Functions (Date and Time, Statistical, Logical and Mathematical) -
Use of spreadsheet in Business Applications
Payroll Accounting
Asset Accounting -
Graphs and Charts for Business Data
Column chart, Bar chart, Pie Chart, Doughnut chart
Advantages of Graphs and Charts -
Accounting Software Package – GNUKhata
Creation of organisation
Ledger Creation
Voucher entry -
Database Management System
Components of DBMS
Preparation of Table in design view
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two Focus Area - Business Studies
-
Nature and significance of Management
Features of management
Nature of management
Levels of management
Co-ordination and elements -
Principles of management
Fayol’s management principles
Techniques of scientific management -
Business Environment
Importance of environment
Dimensions of environment
Industrial Policy 1991
Liberalisation, Privatisation, Globalisation -
Planning
Features of planning
Steps in planning
Types of plans -
Organising
Importance of organising
Organisational structure and types
Formal and Informal organisation
Delegation and Decentralisation -
Staffing
Steps in Staffing
Sources of recruitment
Selection Tests
Methods of training -
Directing
Elements of directing – Supervision, Motivation, Leadership, Communication
Maslow’s need hierarchy theory
Leadership – qualities of a good leader
Communication – process
Barriers of communication -
Controlling
Steps in controlling
Control by exception
Span of control
Techniques of controlling -
Financial Management
Financial decisions
Capital structure – Factors
Factors determining fixed capital
Factors determining working capital -
Capital Market
Money market – instruments
Capital market – instruments
SEBI – Functions -
Marketing Management
Marketing and selling
Functions of marketing
Marketing mix
Pricing – Factors
Promotion and advertising
Sales promotion -
Consumer protection
Rights of consumers
Name of Acts for consumers
Redressal Forums under CPA
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two Focus Area - Economics
PART 1 - Introductory Microeconomics
| Chapter | Focus Area |
| Chapter 1 Introduction |
1 A SIMPLE ECONOMY2 CENTRAL PROBLEMS OF AN ECONOMY 1.3 ORGANISATION OF ECONOMIC ACTIVITIES 1.3.1 The Centrally Planned Economy 1.3.2 The Market Economy 1.5 MICROECONOMICS AND MACROECONOMICS |
| Chapter 2 Theory of Consumer Behaviour |
2.1 UTILITY 2.1.1 Cardinal Utility Analysis 2.1.2 Ordinal Utility Analysis 2.2 THE CONSUMER’S BUDGET 2.2.1 Budget Set and Budget Line 2.3 OPTIMAL CHOICE OF THE CONSUMER 2.4 DEMAND 2.4.1 Demand Curve and the Law of Demand 2.4.3 Normal and Inferior Goods 2.4.4 Substitutes and Complements |
| Chapter 3 Production and costs |
3.1 PRODUCTION FUNCTION 3.2 THE SHORT-RUN AND THE LONG RUN 3.3 TOTAL PRODUCT, AVERAGE PRODUCT AND MARGINAL PRODUCT 3.4 THE LAW OF DIMINISHING MARGINAL PRODUCT AND THE LAW OF VARIABLE PROPORTIONS 3.7 COSTS 3.7.1 Short-Run Costs |
| Chapter 4 The Theory of the Firm under Perfect Competition | 4.1 PERFECT COMPETITION: DEFINING FEATURES 4.2 REVENUE |
| Chapter 5 Market Equilibrium |
5.1 EQUILIBRIUM, EXCESS DEMAND, EXCESS SUPPLY 5.2 APPLICATIONS |
| Chapter 6 Non-competitive Markets | 6.1 SIMPLE MONOPOLY IN THE COMMODITY MARKET |
PART II - Introductory Microeconomics
| Chapter | Topics to be focused |
| Chapter 1 Introduction | 1.1 EMERGENCE OF MACROECONOMICS |
| Chapter 2 National Income accounting |
2.1 SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF MACROECONOMICS 2.2.1 The Product or Value Added Method 2.2.2 Expenditure Method 2.2.3 Income Method 2.2 CIRCULAR FLOW OF INCOME AND METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME |
| Chapter 3 Money and banking |
3.1 FUNCTIONS OF MONEY 3.2 DEMAND FOR MONEY AND SUPPLY OF MONEY 3.2.1. Demand for Money 3.2.2. Supply of Money |
| Chapter. 4 Determination of Income and employment |
4.1 AGGREGATE DEMAND AND ITS COMPONENTS 4.1.1. Consumption 4.1.2. Investment 4.2 DETERMINATION OF INCOME IN TWO-SECTOR MODEL |
| Chapter 5 Government Budget and the Economy |
5.1 GOVERNMENT BUDGET — MEANING AND ITS COMPONENTS 5.1.1 Objectives of Government Budget 5.1.2 Classification of Receipts 5.1.3. Classification of Expenditure 5.2 BALANCED, SURPLUS AND DEFICIT BUDGET |
| Chapter 6 Open Economy |
6.1 THE BALANCE OF PAYMENTS 6.1.1 Current Account 6.1.2 Capital Account |
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two Focus Area - Computer Application (Commerce)
| Chapter | Focus Area |
| 1. Review of C++ Programming | Tokens, Data types, Control statements. Simple programs may be asked. |
| 2. Arrays | Syntax to declare an array, Accessing of elements, String handling, I/O functions to handle strings. No programs required |
| 3. Functions | Built-in functions (Name and use only), Call by value and Call by reference method. No programs required |
| 4. Web Technology | Static and Dynamic web pages, Comparison of Client-side and Server-side scripts, Structure of HTML code, Container tags and empty tags, Common attributes of <BODY> tag, Use of important tags(Headings, <BR>, <P>, <HR>, text formatting tags, <MARQUEE>, <FONT>,<IMG>), Only the essential attributes need to be considered. |
| 5. Web Designing using HTML | List (Ordered, Unordered, Definition), <A> tag and HREF attribute, Definition of internal and external linking, Table tags, Listing and use of Input controls in Form, Coding questions may focus only on simple lists and simple tables. |
| 6. Client-side Scripting using JavaScript | <SCRIPT> tag, Data types, var keyword, Operators, Control structures and Built-in functions |
| 7. Web Hosting | Types of web hosting, FTP client software, Free hosting |
| 8. Database Management System | Advantages of the database, Components of DBMS, Types of users, RDBMS terminologies, Relational operations (Select, Project, Union, Intersection) |
| 9. Structured Query Language | SQL components, SQL data types. Constraints, Use of commands (DDL-CREATE TABLE, DROP TABLE; DML – SELECT, DELETE, UPDATE with essential clauses only). SQL queries are to be avoided. |
| 10. Enterprise Resource Planning | Functional units of ERP(listing only), Examples for ERP packages, Benefits of ERP. |
| 11. Trends and Issues in ICT | Mobile communication services, Short notes on mobile OS, Cybercrimes against individuals. |
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two Focus Area - Statistics
-
Meaning of Correlation,
Types of Correlation – Positive, Negative, Zero. Methods of studying Correlation – Scatter diagram, coefficient of correlation. Karl Pearson’s coefficient of correlation, Spearman’s Rank correlation ( non repeated only). -
Regression Analysis
Concept of Regression, Regression Lines, Equation of Regression lines. Properties of regression coefficients. Identification of Regression Lines. -
Elementary Calculus
First derivative and Second derivative of simple linear functions. Maxima and Minima (problems). Integration of simple functions. Definite integrals -
Random Variables
Random Variables- Discrete and Continuous. Discrete Random Variables -Probability mass function (pmf), Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF). Mean. Variance and their properties. Continuous Random Variables – Probability density function (pdf), problems based on properties of pdf. -
Discrete Probability Distributions
Binomial Distribution-pmf. mean and variance, problems
Poisson Distribution- pmf, mean and variance, problems -
Normal distribution
Normal Probability Density function, Mean and variance, Normal curve and its properties, Standard Normal Distribution, Z-transformation and Z-Score, Standard Normal Tables, simple problems based on std Normal tables. -
Sampling Distributions
Parameter and Statistic. Sampling Distribution. Determination means of the sample mean (SRSWOR). -
Estimation of parameters
Statistical inference, Estimation of Parameters, Point Estimation, Properties of a Good Estimator -Unbiasedness. Consistency, Sufficiency and Efficiency. -
Testing of Hypothesis
Statistical Hypothesis. Test statistic and Critical Region.Type I and Type II Errors, Level of Significance and Power of Test, Test for significance of Single Mean ( large sample only). -
Analysis of Variance
Causes of variations. Assumptions underlying ANOVA, One-way classification by using ANOVA Table. -
Statistical Quality Control
Meaning of Quality, Causes of variations. Variable Control Charts (xchart only) -
Time Series Analysis
Components of Time series. Trend analysis- Method of semi averages, moving averages. -
Index Numbers
Types of Index numbers- Simple Index Number (Simple AM), Simple Aggregate Method. Weighted Index number ( Laspayre’s, Paasche’s, Fisher’s Index Numbers). Uses of Index Numbers.
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two ( Humanities ) Focus Area
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two Focus Area - History
| Name of the Themes | Focus Area |
| Bricks, Beads and Bones | Subsistence Strategies – Mohenjodaro – A planned urban centre – Social differences – Craft production – Procuring materials – Seals, script and weights – Decline |
| Kings, Fanners and Towns | Rise of Magadha – Mauryan empire – New notions of kingship – Towns and trade – Limitations of inscriptional evidence |
| Thinkers, Beliefs and Buildings | Sacrifices and debate – Buddha – Mahavira – Stupas – Mahayana Buddhism. |
| Through the Eyes of Travellers | Al-Biruni – Ibn Battuta – Francois Bernier |
| An Imperial Capital – Vijayanagara | Capital and its environs – Royal Centre – Sacred Centre |
| Rebels and the Raj | Leaders and followers – Rumours and prophecies – Images of the revolt |
| Mahatma Gandhi and the Nationalist Movement | Early struggles – Non-co-operation – Salt Satyagraha – Quit India |
| Kerala Towards Modernity | Early resistance – Social reform – Struggle for a Democratic Society |
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two Focus Area - Political Science
| Name of the Chapters | Focus Area |
| Challenges of Nation Building |
1. Challenges for the new Nation 2. Three Challenges 3. Partition – process and consequences 4. Integration of Princely States 5. Reorganization of States |
| Era of One-PartyDominance |
1. Challenges of Building Democracy 2. Congress Dominance in the first three general elections 3. Nature of Congress Dominance 4. Congress as Social and Ideological coalition 5. Opposition Parties – Socialist Party, Communist Party of India, Swatantra Party, Bharatiya Jana Sangh |
| India’s External Relations |
1. Policy of Non-Alignment – Nehru’s Role, Distance from two blocs, Afro
Asian Unity 2. Peace and Conflict with China 3. Wars and Peace w with Pakistan 4. India’s Nuclear Policy |
| The Crisis of Democratic Order |
1. Background to Emergency Economic Context Gujarat and Bihar Movements Conflict with Judiciary Declaration of Emergency 2. Consequences of Emergency 3. Controversies regarding emergency – What happened during an emergency? 4. Lessons of Emergency 5. Loksabha Elections 1977 – Janata Government |
| Rise of Popular Movements |
1. Chipko Movement 2. Dalit Panthers 3. Bharathia Kisan Union 4. Anti–Arrack Movement 5. Narmada Bachao Aandolan 6. Lessons of Popular Movements |
| Regional Aspirations |
1. Jammu and Kashmir 2. Punjab 3. The North East 4. Dravidian Movement 5. Lessons of Regional Aspirations |
| End of Bipolarity |
1. Soviet System 2. Why did the Soviet System disintegrate? 3. Consequences of disintegration 4. Shock Therapy – Consequences |
Kerala Higher Secondary Plus Two Focus Area - Computer Application (Humanities)
| Chapter | Focus Area |
| 1. Introduction to Publishing | DTP Software, Elements of design. Principles of design. Electronic publishing(Web-based. Digital distribution) |
| 2. Introduction to Word Processors | Features of a word processor, Libre Office Writer IDE Components, Short-cut key$(New, Save, Open, cut, copy, paste, undo, print), Navigation keys, Header and Footer, comparison of cut-paste and copy-paste, Drop Caps, Indents- Types only, Page orientation-Portrait, Landscape |
| 3. Creating Professional Documents | Tables(Creating a table. Borders to tables, Managing tables), Inserting graphics(Adding an image, Using drawing tools, Inserting charts), Inserting page borders. Inserting watermarks, Converting text to a table, Splitting text into columns, Mail merge( Definition and Steps only) |
| 4. Web Technology | Static and Dynamic web pages, Comparison of Client-side and Server-side scripts, Structure of HTML code, Container tags and eC? pty tags, Common attributes of <BODY> tag, Use of important tags(<P>,<BR>, Heading Tags, text formatting tags,<MARQUEE>,<FONT>,<IMG>) covered in this chapter, Only the essential attributes need to be considered. |
| 5. Web Designing using HTML | List (Ordered, Unordered and Definition), <A> tag and HREF attribute, Definition of internal and external linking, ‘fable tags, Coding questions may focus only on simple lists and tables. |
| 6. Cascading Style Sheet | Advantages of using CSS, Ways to add CSS to a web page(names only-Internal style sheet, External style sheet. Inline style) |
| 7. Web Hosting | Types of web hosting, FTP client software, Free hosting |
| 8. Database Management System | Advantages of DBMS, Components of DBMS, Users of Database, RDBMS terminologies |
| 9. Structured Query Language | SQL components, SQL data types, Use of commands (DDL- CREATE TABLE, DROP FABLE, DML- INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE-with essential clauses only).SQL queries arc to be avoided. |
| 10. Trends and Issues in ICT | Mobile communication services. Mobile Operating systems, Cybercrimes against Individuals |
Plus Two Related Links
| Plus Two Study Materials | Click Here |
| Plus Two Textbook Solutions | Click Here |
| Plus Two Focus Area | Click Here |
| Plus Two Previous Year Questions with Solution | Click Here |
| Plus Two Textbook PDF | Click Here |
Other Related Links
| Plus Two Physics | Click Here |
| Plus Two Chemistry | Click Here |
| Plus Two Mathematics | Click Here |
| Plus Two Botany | Click Here |
| Plus Two Zoology | Click Here |
| Plus Two Computer Science | Click Here |
| Plus Two English | Click Here |